In this article we will further explain every part of working with W3Grid. Make sure to read Part 1 before reading this article.
1. Working with rows
Beside the AddRow method, rows may be added by using the InsertRow method. With this method row may be added at any position, not only at the end.
Example:
W3Grid1.InsertRow(5);
InsertRow method also updates the LastAddedRow property.
To delete a specified row call:
DeleteRow(RowIndex);
Before deleting a row it is recommend to check if row’s index is valid:
if W3Grid1.RowExist(IndexToDelete) then W3Grid1.DeleteRow(IndexToDelete);
To delete all rows in a grid call method ClearRows. This method delete only rows, column structure will remain intact.
Every TW3Row is a standalone object (TW3CustomControl descendant) and it may be accessed via the Row array property. Handy (read-only) property RowCount may be used to iterate trough all rows.
Example:
procedure TForm1.W3Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
i: Integer;
begin
for i := 0 to MyGrid.RowCount - 1 do
if i mod 2 = 0 then
MyGrid.Row[i].Color := clCream;
end;In this example we are painting every second row in different color.
2. Working with cells
As mentioned in the first article, a cell may be accessed via the Cell array property.
In W3Grid, every cell is a TW3CustomControl descendant. You may therefore typecast the Cell property to TW3CustomControl to access its properties and methods.
Example:
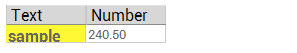
(MyGrid.Cell[0, 0] as TW3CustomControl).Color := clYellow; (MyGrid.Cell[0, 0] as TW3CustomControl).Font.Weight := 'bold'; (MyGrid.Cell[0, 0] as TW3CustomControl).Font.Size := 16;
Result:
By using TW3CustomControl methods you may also adjust child controls within a cell (e.g. progress bar inside a TW3ProgressColumn, toggle switch inside a TW3ToggleSwitchColumn and similar).
3. Working with Columns
Beside properties and methods, some column types offer events which can be handled in your code. For example, you may want to respond when user clicks on a button inside a TW3ButtonColumn, or toggle a switch inside a TW3ToggleSwitchColumn.
At the moment, Column event handlers must be created manually.
procedure TForm1.InitializeForm; begin inherited; MyButtonColumn.OnButtonClick := W3ButtonColumnButtonClick; // link to handler end; procedure TForm1.W3ButtonColumnButtonClick(Sender: TObject) begin // event handler - your code here end;
Design-time editor is planed for future releases.

Hi,
I created an Android application with Smart Mobile Studio with remote pagination and filtering.
I would like to know if I can create using pure Smart solution?
See at:
[url]http://youtu.be/IVARdw473mc[/url]